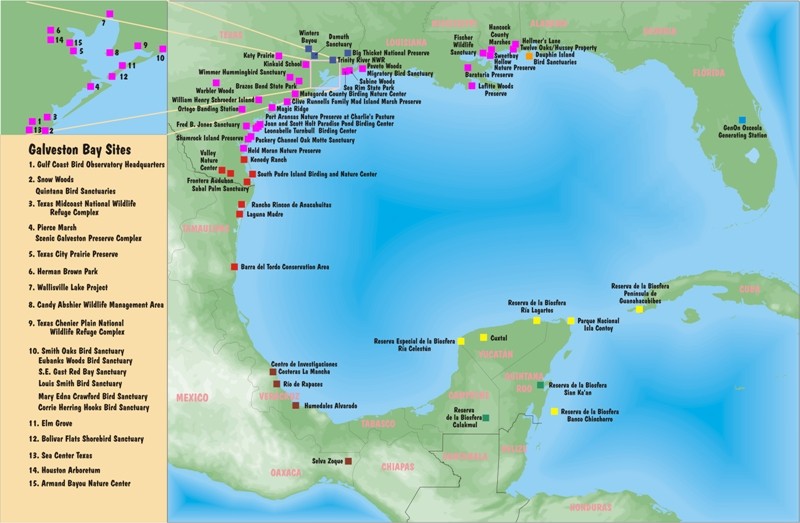
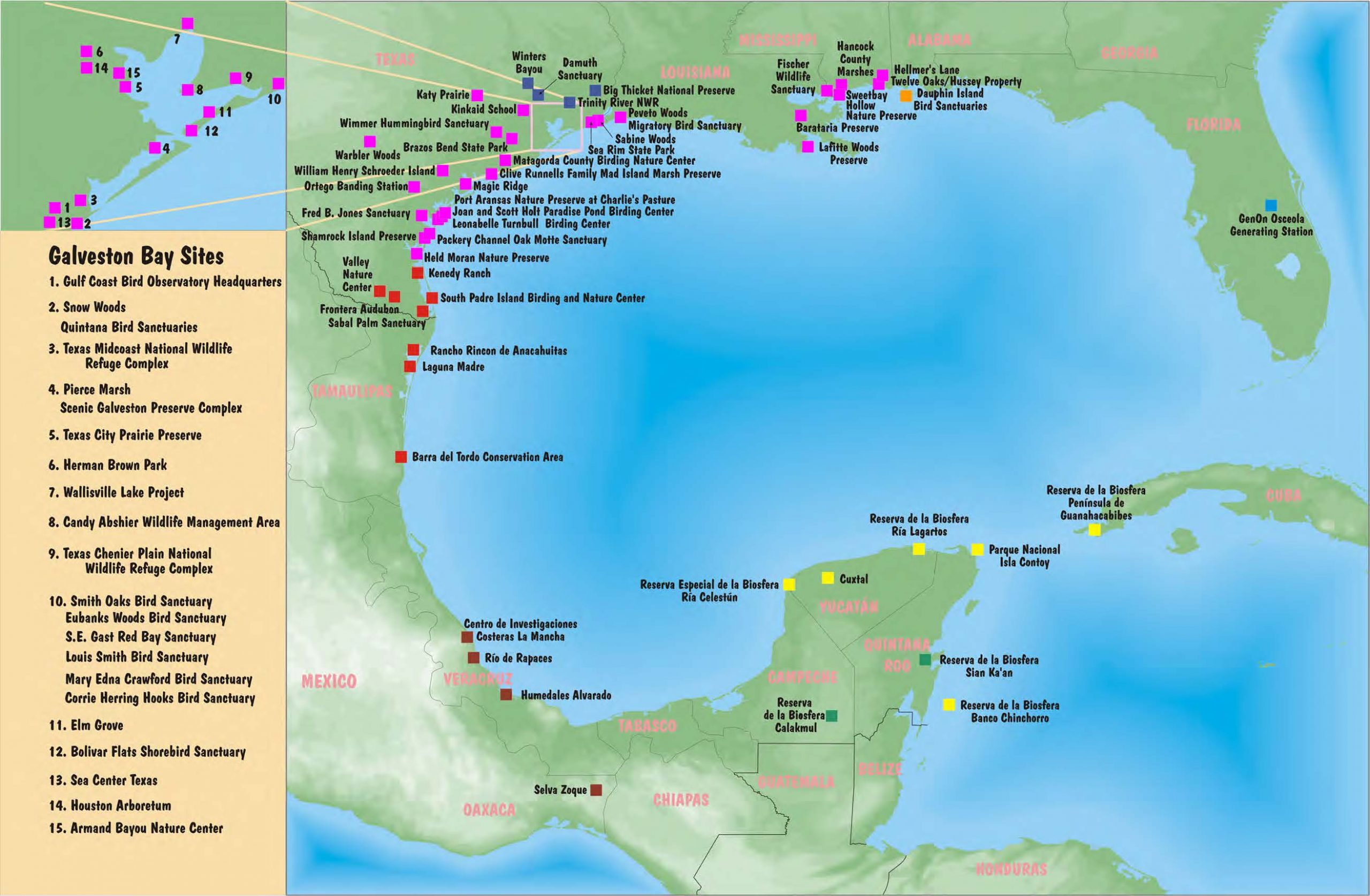
Gulf Coast Bird Observatory’s Site Partner Network
The Site Partner Network (SPN) was GCBO’s original conservation program, a Gulf-wide network of partners located in each of the US and Mexican states that border the Gulf of Mexico, and in Cuba. There were over 70 sites in the network, all of whom share the common goal of preserving and restoring essential migratory bird habitat for the 300 plus species of birds that we share. Among the partners, more than 9 million acres of precious wetland, forests, coastal prairies and other critical habitats is protected. From as far east as Florida and Cuba, across the Gulf to Texas and Mexico and south to the Yucatan Peninsula GCBO worked to connect this network across state, international, and language boundaries. No observatory before had taken on the task of linking sites to make a “string of pearls,” a chain of special and important bird habitats along the coast such as this. The SPN still exists in the sense that many of the original network sites still work together on projects and partnerships. The SPN is no longer an active GCBO project due to changes over time in the partner’s needs, conservation tools, and available assistance to organizations. We celebrate the huge success that the SPN had in linking partners, help fund conservation work and land conversation, and bringing the bigger picture of Gulf wide conservation needs to the forefront.
Peninsular Florida
Peninsular Florida connects subtropical and temperate climate zones. More than 40 habitat types can be found here, including beach and dune, river watersheds, xeric scrub uplands, freshwater marshes, sawgrass and cypress wetlands, extensive coastal mangroves and salt marsh, expanses of seagrass beds and unique pine rocklands and tropical hardwood hammocks.
East Coast Gulf Plain
The East Gulf Coastal Plain ecoregion encompasses portions of five states and over 42 million acres from the southwestern portion of Georgia across the Florida Panhandle and west to the southeastern portion of Louisiana. It is physically characterized by soils derived primarily from unconsolidated sands, silts, and clays transported to the area by rivers from the Appalachian Mountains. Land forms include rolling longleaf pine-dominated uplands to pine flatwoods and savannas, seepage bogs, bottomland hardwood forests, barrier islands and dune systems, and estuaries.
Coastal Prairies
The Coastal Prairie is located along the western Gulf coast just inland from the coastal marsh. It once extended from Lafayette, Louisiana to Corpus Christi, Texas but has been reduced substantially due to development. It includes not only coastal prairie grasslands similar to the tallgrass prairies of the Midwestern United States but also coastal wetlands and forested wetlands including Columbia Bottomland Hardwood forest.
West Gulf Coastal Plain
The West Gulf Coastal Plain covers more than 52 million acres and is an area of gently sloping terrain that extends from Georgia to Texas. It lines inland from the Coastal Prairies and consists of bottomland forests and associated wetlands. The predominant forest type is loblolly-shortleaf pine but forest wetlands contain oak, hickory, and gum type forests.
South Texas Brushlands
The South Texas Brushlands extend into the subtropical regions of the Lower Rio Grande valley. Much of the area is dominated by mesquite, acacia, prickly pear, lotebush, granjeno, white-brush, Texas ebony and wild olive which form dense thickets. It is a biological diverse habitat that includes tropical, grassland, and desert bird species.
Tropical Wet Forests
Tropical wet forests are characterized by high precipitation and humidity and have plants with broad leaves that fall off throughout the year. This is because rather than the four seasons that occur in deciduous forests, tropical wet forests have two seasons, wet and dry. Tropical wet forests have little variation in seasonal temperatures which allows plant growth year round. Because of this they support very high densities of plant and animal communities.
Yucatan Moist Forest
Yucatan moist forest is found on the Yucatan Peninsula in southern Mexico, northern Guatemala, and northern Belize and has a tropical humid climate with high biodiversity. It consists of tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests with little topographic relief.